
A Holistic Approach
Most clients who struggle with medical adherence and/or the lifestyle improvements recommended by their treatment team (the Lifestyle Prescription) benefit from the structure that wellness coaching provides as well as the power of the coaching alliance. Clients are attempting to adopt new behaviors, shift from old unhealthy behaviors, and often reorganize their lives radically to do so. They benefit from co-creating, with their coach, a well-designed plan that addresses their overall, total wellness, and makes medical adherence a part of it. It becomes just one Area of Focus in a fully-integrated Wellness Plan.
Health and wellness coaches who work with clients challenged by chronic illness, and even more acute medical challenges, are counted upon to help with medical compliance and adherence. The clients themselves count on them because they struggle with medical self-testing, taking medication properly, following up with appointments, exercising, and whatever the recommendations of their “lifestyle change prescription” are. Coaches are also counted upon by those providing healthcare services, insurance services, employee benefits and more, to help manage costs through better overall patient compliance/adherence. This often becomes a large part of a wellness coach’s job.
The job is valued because the need is great. First of all, when clients fail to take their medication properly, manage their blood sugar levels well by doing their self-testing regularly, etc., they suffer. There are more hospitalizations and trips to the emergency room, more chance of complications and usually more progression of progressive diseases.
The Network for Excellence in Health Innovation calls improving patient medical adherence a $290 Billion Opportunity. (https://www.nehi.net/bendthecurve/sup/documents/Medication_Adherence_Brief.pdf) that’s what is lost in U.S. healthcare spending each year due to poor medication adherence alone. The same source goes on to say that “when patients with severe or chronic conditions do not take their medications, the consequences can be extreme. Clinical outcomes are highly affected by non-adherence. For example, those with 80-100 percent adherence rates are significantly less likely to be hospitalized than their counterparts.”
Lack of follow through on medications, and other types of “following doctor’s orders” can be due to many different reasons, some of which are not the fault of the patient. Cost of prescriptions and supplies in the United States is often a big factor. Inadequate instructions from the healthcare provider, a lack of self-care education, access to treatment and/or education, plus costs, account for about 31% of the reasons for poor adherence. The other “69% of the problem is behavioral, such as perceived benefits, poor doctor-patient relationship, medication concerns, or low self-efficacy.” (http://www.dtcperspectives.com/impact-behavioral-coaching-adherence/#_edn3).

A note on terms:
Non-compliance — not complying with medical directives, prescriptions, etc.
A patient decides that their physician is basing a prescription on inadequate information and decides not to take prescribed statins.
Non-compliance — More of a refusal, a decision. Can be medical or lifestyle prescriptions. May be due to external causes (like cost). More authoritarian.
Non-adherence — not following through consistently with the treatment plan including the “lifestyle prescription”. Not adhering to the plan. More likely due to inabilities, difficulties executing the plan, etc.
You will also find that the terms are sometimes interchangeable in the professional literature.
Research on health and wellness coaching has shown significant effectiveness in improving this problem. Unfortunately, most of the research narrowly focuses on one research variable, one aspect of medical compliance/adherence – medication adherence. In a study of the impact of health coaching with patients with poorly controlled diabetes, hypertension, and/or hyperlipidemia, “Health coaching by medical assistants significantly increases medication concordance and adherence.” (1) Ruth Wolever and Mark Dreusicke (2) found that integrative health coaching led to an increase in medication adherence and that better adherence correlated with a greater decrease in HbA1c (blood sugar measure).
Many of the studies are gleaning what appear to be the coaching methods that make a real difference in effectiveness. Wolever and Dreuskicke concluded that “Medication adherence requires underlying behavior skills and a supporting mindset that may not be addressed with education or reminders.” So, though helpful, clients/patients often need more than just text messages sent on their smart phones. Amanda Rhodes, in a 2017 article (3) takes on a more corporate perspective in showing how coaching is beneficial to both patients and the pharmaceutical and healthcare companies that serve them. What their research emphasized was how client-centered the whole approach needs to be. “Patient-centered behavioral coaching is designed to help patients determine the way in which THEY believe they need to change their behaviors to achieve their goals. Patients who feel listened to are more comfortable with the care they receive and are more likely to adhere.”
Alliance Over Compliance
For the health/wellness coach and the client they serve, the heart of the matter is the coaching alliance. As seen in the articles we’ve spotlighted here, adherence comes not from medical admonishment or authoritarian directives. It comes from a client/patient developing self-determined goals that they are motivated to pursue. It comes from having an ally to help them navigate through the barriers that they face to achieving the high level of health and wellness that all people want. The coach may be well aware of the medical urgency for a client to, for example, quit smoking, or take their medication properly. But, as we’ve learned from all forms of behavioral change efforts, the process, ultimately, must be self-directed. That is, the client has to see the value in making the change, be ready to make it, and have both a concrete plan of action and the support they need to achieve it. Tempting as it may be for the coach to become extremely directive and take over the action planning, they must remain in a true coaching mindset and be the ally the client needs in their own process. This requires patience, but as is often the case, patience pays off.
A Fully Integrated Wellness Plan
The client and coach work together to determine what the other Areas of Focus will be, based upon Readiness for Change Theory, the directives of the Lifestyle Prescription, the values and interests of the client, and all of the exploration and assessment that the coach and client have done together. Other Areas of Focus could include such things as: Attaining & Maintaining A Healthy Weight; Smoking Cessation; Achieving Greater Social Support, etc.
Areas of Focus break down into Goals and the specific Action Steps that the client will engage in to achieve those goals. All of this is co-created, not dictated.
Coaching Does What It Is Good At
In the focus on medical adherence, coach and client co-create a way to identify the specific behaviors that are needed to either develop or change. They then, strategize the best Action Steps that will be an optimal starting point for success. They develop tracking strategies, so the client will know when they are being successful at doing their self-testing regularly, taking medication on time, staying organized enough to follow through on medical appointments, etc. The key to tracking, whether done on phone apps, or good old pencil and paper is following up with Accountability on it. Sending the coach app or text messages, or simply reporting in at the next coaching appointment will help the client feel accountable to themselves to achieve what they, themselves, want to get done. The coaching alliance also takes on the myriad barriers, both internal and external that get in the way to solid medical adherence. Strategizing through barriers such as a lack of family or workplace support, checking out fearful assumptions (especially about side-effects), all increase the likelihood of success.
Astonishing Noncompliance
There are times when we see a complete shutdown of efforts to follow the directives of the treatment team, especially around the lifestyle changes that are urgently needed to shift. This refers to a client paralyzed by grief over their perceived loss of health. To understand this check out our previous blog post – “Astonishing Non-compliance – Understanding Grief and Readiness for Change in the Health Challenged Client” (https://wp.me/pUi2y-n2 ).
The Many Faces of Medical Adherence
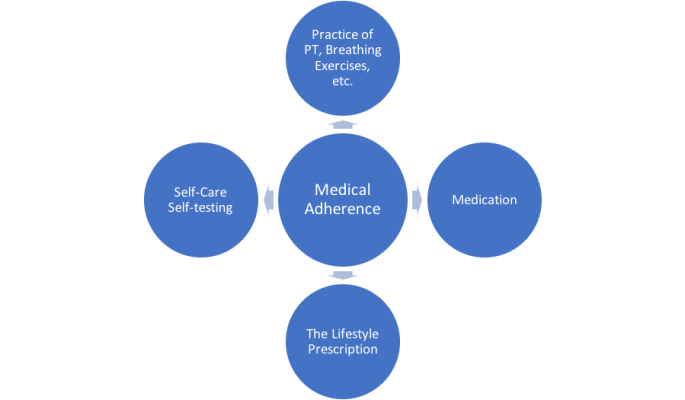
Coach with your client to determine what the components of medical adherence are for them. Don’t just focus on medication. Help them see that their best strategy is to live their healthiest life possible in all dimensions of their wellness.
RESOURCES
(1) Thom D, Willard-Grace R, Hessler D, DeVore D, Prado C, Bodenheimer T, Chen E. The impact of health coaching on medication adherence in patients with poorly controlled diabetes, hypertension, and/or hyperlipidemia: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Board Fam Med. 2015 Jan-Feb;28(1):38-45. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2015.01.140123
(2) Ruth Q Wolever, Mark H Dreusicke.
Integrative health coaching: a behavior skills approach that improves HbA1c and pharmacy claims-derived medication adherence. Clinical care/education/nutrition/psychosocial research. https://drc.bmj.com/content/4/1/e000201
(3) The Impact of Behavioral Coaching on Adherence
by Amanda Rhodes on June 29, 2017 in DTC in Focus, DTC News
http://www.dtcperspectives.com/impact-behavioral-coaching-adherence/#_edn3
Additional Resources
• Sforzo, Kaye, Todorova, et al. (2017). Compendium of the Health and Wellness Coaching Literature. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine,1559827617708562. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1559827617708562
• Ruth Q. Wolever, Making the Case for Health Coaching: How to Help the CFO Understand — Real Balance Coach Center – April 2018 Free Monthly Webinar.
• https://ichwc.org/resources/ “A Systematic Review of the Literature on Health and Wellness Coaching: defining a Key Behavioral Intervention in Healthcare” (Resources section for ICHWC)






 4) Be Their Ally.
4) Be Their Ally.
